In 2025, the United States took a decisive step in the history of digital assets with the adoption of the Genius Act — short for Guiding and Establishing National Innovation for U.S. Stablecoins.
This legislation marks the first comprehensive federal framework regulating stablecoins, those digital assets pegged to real-world currencies such as the U.S. dollar.
Championed by Republican Senator Bill Hagerty and supported by President Donald Trump, the Genius Act pursues three goals: restoring trust in a sector shaken by scandals, stabilizing a rapidly growing market, and reaffirming U.S. monetary sovereignty in the global race for digital currencies.
Concretely, the law requires stablecoin issuers to hold 100% reserves, operate under a federal license, and publish regular audit reports.
A strict framework — but one presented as necessary to position the digital dollar at the center of global digital finance.
Its adoption marks a turning point: just as Europe completes the rollout of its MiCA regulation, Washington regains the initiative with a framework designed to dominate the global stablecoin market and attract crypto companies back to U.S. soil.
The Genius Act therefore does more than regulate a digital asset — it redefines America’s financial strategy for the decade ahead.
Explore the full analysis from our stablecoin experts.
Article Summary
The Genius Act establishes the first comprehensive federal regulatory framework for stablecoins in the United States.
Its aim: restore trust, support responsible innovation, and reinforce the U.S. dollar as the backbone of global digital finance.
A foundational law that transforms stablecoins into regulated monetary instruments — blending innovation with strategic geopolitical intent.
Context: Why the U.S. urgently needed a federal stablecoin framework
A booming market
Since 2020, the stablecoin market has become one of the pillars of global digital finance.
These cryptocurrencies pegged to stable assets — most often the U.S. dollar — have found widespread use in DeFi, cross-border payments, and corporate treasury management.
Between 2020 and 2025, adoption exploded: from retail users to major financial institutions, stablecoins became the go-to tool for fast transfers, hedging crypto volatility, and accessing decentralized yield.
By 2025, total market capitalization exceeded $300 billion, up 73% year-over-year.
This spectacular growth attracted capital and innovation — but also growing concerns.
Unregulated risks
Until recently, the U.S. had no unified federal regulation governing stablecoins.
Each state issued its own licenses or authorizations, resulting in a fragmented and inconsistent regulatory patchwork.
This vacuum allowed opaque actors and risky models to flourish.
The most infamous example: the collapse of TerraUSD (UST) in May 2022 — an algorithmic stablecoin designed to maintain a 1:1 peg with the dollar.
Its sudden crash erased over $40 billion in a matter of days and sent shockwaves through the entire crypto ecosystem.
The episode highlighted the dangers of a market operating without safeguards:
- extreme volatility
- lack of transparency around reserves
- risks of fraud, money laundering, and systemic contagion
A need for trust and oversight
In this environment, the need for strong federal rules became undeniable.
The Genius Act addresses this need head-on: it aims to build trust in digital assets while enabling responsible innovation.
Its core ambition is to create a sustainable ecosystem where every stablecoin issuer is clearly identified, audited, and accountable to federal authorities.
The approach seeks to balance financial stability, user protection, and technological growth — without suffocating innovation.
💡 Key Fact
Before the Genius Act, each U.S. state enforced its own crypto rules.
The result: a fragmented regulatory landscape that was difficult for companies to navigate — and even harder for authorities to oversee.
The Genius Act unifies this system by creating the first nationwide federal framework for stablecoins.
The Genius Act
Definition
Signed into law in July 2025, the Genius Act — Guiding and Establishing National Innovation for U.S. Stablecoins — is the first federal U.S. legislation dedicated specifically to regulating payment stablecoins.
Until now, the market operated in a legal grey zone, with issuers relying on state-level licenses that were often inconsistent across jurisdictions.
This landmark bill closes that gap by establishing a single, transparent, and tightly supervised federal framework.
Its core objectives are to:
- protect consumers,
- stabilize the digital monetary system,
- and reinforce the dominance of the U.S. dollar in an increasingly digital global economy.
The Genius Act is therefore not just another “crypto law.”
It is an economic and geopolitical instrument designed to position the United States as the global leader in regulated digital finance.
A law designed for stability and sovereignty
The Act introduces a clear distinction between payment stablecoins — treated as monetary instruments — and all other digital assets (yield tokens, NFTs, speculative crypto-assets), which fall under separate regulatory frameworks.
Issuers of these payment stablecoins must:
- hold 100% reserves,
- publish monthly reports verified by an accredited auditor,
- operate under a federal license issued by the Federal Reserve (for banking entities) or the OCC (for licensed non-bank issuers),
- and comply with Bank Secrecy Act requirements, including AML/CFT obligations.
Beyond regulation, the law serves a political purpose:
by anchoring the U.S. dollar at the center of global digital transactions, the Genius Act aims to prevent the rise of competing currencies (such as China’s digital yuan or unregulated offshore stablecoins).
Genius Act Summary Sheet
| Element | Detail |
| Adoption | June 2025 (Senate: 68 votes in favor), officially signed in July 2025 |
| Led by | Senator Bill Hagerty (R-Tennessee), supported by the White House and Donald Trump |
| Scope | Stablecoins backed by fiat currencies (USD, gold) and used for payments or treasury management |
| Supervision | Federal Reserve (bank issuers) & OCC (licensed non-bank issuers) |
| Objectives | Financial stability, reserve transparency, monetary sovereignty, consumer protection |
| Key obligations | 100% reserves, monthly public audits, federal licensing, ability to freeze funds upon court order |
| Indirect targets | Tether (USDT), Circle (USDC), financial institutions, and digital payment platforms |
| Strategic outcome | Maintaining global dollar dominance and attracting crypto innovation to the U.S. |
💡 Good to know
The Genius Act is often described as the U.S. counterpart to the European MiCA regulation.
But while Europe seeks a balance between stability and innovation, the U.S. approach is more assertive and dollar-centric: protect the dollar while institutionalizing crypto.
In other words, Washington does not aim to ban stablecoins — it aims to absorb them into the American financial system.
Core Principles of the Genius Act
Réserves à 100 % et actifs autorisés
100% Reserves and Authorized Assets
At the heart of the Genius Act lies a simple but strict rule: every stablecoin in circulation must be fully backed by real, liquid assets.
In other words: 1 stablecoin = 1 dollar.
This requirement is designed to restore trust in a market shaken by past scandals. Issuers must be able to prove—at any moment—that all tokens in circulation are backed by an equivalent amount of high-quality reserves.
The law strictly defines which assets can be used as backing:
- Dollar-denominated bank deposits held in insured financial institutions
- U.S. Treasury bills with a maximum maturity of 93 days
- Government money market funds
- Repurchase agreements (repos) backed by Treasury securities
Any asset considered risky, illiquid, or speculative—private bonds, equities, cryptocurrencies, structured products—is explicitly prohibited.
This framework turns compliant stablecoins into secure monetary instruments, aligned with U.S. banking standards.
Transparency and Auditing
Transparency is a cornerstone of the Genius Act.
Every stablecoin issuer must publish a monthly public report detailing:
- the total number of tokens in circulation,
- the exact composition of the reserves,
- and the current market value of those reserves.
Issuers holding more than $50 billion in outstanding stablecoins are also subject to an annual mandatory audit performed by an independent, accredited accounting firm.
This reporting regime aims to bring institutional-grade trust to the market, similar to the oversight imposed on publicly traded banks. Stablecoins effectively become continuously monitored, audited digital monetary instruments.
Issuer Requirements
The law puts an end to the era when virtually anyone could launch a stablecoin.
The Genius Act restricts issuance to three categories of regulated entities:
- Banks and their subsidiaries
Allowed to issue stablecoins under Federal Reserve supervision. - Non-bank issuers licensed by the OCC
Payment companies or blockchain firms, subject to strict oversight and recurrent audits. - State-level issuers
Authorized to issue up to $10 billion in stablecoins; beyond that threshold, they fall under full federal regulation.
This multi-layer system preserves innovation and competition while ensuring that every issuer meets a unified national compliance standard.
💡 Key Insight
The Genius Act explicitly bans algorithmic stablecoins, such as TerraUSD (UST), whose value relied on market incentives rather than real reserves.
Only stablecoins backed by verifiable, high-quality assets are permitted in the United States.
This makes the Genius Act a pioneering model of “digital monetary compliance”, unprecedented in scope and ambition.
Consumer Protection and Compliance
Priority repayment in case of bankruptcy
The Genius Act introduces an unprecedented level of protection for stablecoin holders:
in the event an issuer goes bankrupt, users must be reimbursed first — ahead of all other creditors, including shareholders and suppliers.
This provision places stablecoin holders in a position similar to insured bank depositors, although they do not benefit from public protection such as FDIC insurance.
The law also imposes a strict structural rule: a complete segregation between customer funds (the stablecoin reserves) and the issuer’s own corporate funds.
This means no company is allowed to use user deposits to finance internal operations or speculative activities.
Ban on remuneration
The Genius Act prohibits any form of yield on stablecoins.
Issuers are not allowed to offer:
- interest,
- bonuses,
- or derivative products tied to the stablecoin.
The goal is twofold:
- prevent confusion with regulated savings accounts or financial products,
- avoid speculative mechanisms that have led to collapses in the past.
Stablecoins under the Genius Act are therefore pure payment instruments, not disguised investment products.
Compliance obligations (AML / BSA)
The Genius Act aligns stablecoin issuers with U.S. banking-sector standards by requiring compliance with the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) and AML/CFT regulations.
Each issuer must:
- apply strict KYC procedures,
- report suspicious activity to financial authorities,
- maintain the technical ability to freeze, block, or burn tokens under court order,
- ensure full traceability of all transactions.
Supervision is handled through a three-way coordination between:
- the Federal Reserve,
- the U.S. Treasury,
- and the FDIC.
This framework places stablecoin issuers under the same regulatory expectations as traditional financial institutions, establishing an unprecedented level of oversight within the crypto industry.
⚠️ Disclaimer
The information in this article is provided for general informational purposes only.
It does not constitute investment advice, legal advice, or tax guidance.
Businesses and investors should assess their own regulatory obligations before engaging with digital assets.
A Geopolitical Weapon in Service of the U.S. Dollar
Behind its technical appearance, the Genius Act is far more than a financial reform:
it is a geopolitical instrument designed to reinforce American monetary dominance.
By requiring that all regulated stablecoins be backed by U.S. assets — primarily dollars and short-term Treasury bills — the law creates a mechanical support mechanism for federal debt.
Each new stablecoin issued generates additional demand for U.S. government securities, providing the federal government with low-cost financing.
In practice, regulated stablecoins become indirect engines of demand for the dollar, strengthening U.S. economic sovereignty.
On the international stage, the Genius Act also aims to reassert U.S. leadership over global digital-asset regulation.
While Europe advances with MiCA and China rolls out its digital yuan (e-CNY), the United States intends to position itself as the central hub of regulated digital finance.
The intention is clear:
to make the dollar the unavoidable reference for digital payments — even when transactions occur through privately issued instruments such as stablecoins.
💬 Official Quote
“The GENIUS Act will make America the undisputed leader in digital assets.” — The White House, July 18, 2025
The impact on the crypto ecosystem
The winners
The implementation of the Genius Act significantly reshapes the competitive landscape across the crypto industry.
The first beneficiaries are the players already aligned with U.S. regulatory expectations:
- Tether (USDT) and Circle (USDC) — whose reserves are largely backed by short-term U.S. Treasury bills and audited on a regular basis — now stand as reference models for compliance under the new framework.
- Large U.S. banks also gain from this shift: the new rules open the door to issuing tokenized dollars through dedicated subsidiaries and developing new payment or treasury-management services built on regulated stablecoins.
In other words, the Genius Act institutionalizes the stablecoin market by bringing it closer to the traditional banking sector.
The losers
On the other hand, the cost of compliance — audits, monthly reporting, AML/KYC procedures — creates a major barrier for startups and early-stage Web3 companies.
Many younger projects will either need to operate under the umbrella of a regulated entity or simply leave the U.S. market.
Fully decentralized DeFi protocols are also excluded:
without a legal entity or a centralized governance structure, they cannot meet the registration requirements imposed by the Genius Act.
This could push a significant portion of innovation to relocate abroad, particularly toward Asia or Europe, where the regulatory frameworks differ.
Indirect effects on DeFi
Still, the Genius Act is likely to produce indirect effects on decentralized finance.
By introducing regulated, audited stablecoins recognized by the Federal Reserve, the law creates a new trust layer that certain protocols may leverage to attract institutional capital.
Overall yields may decrease — regulated stablecoins leave less room for aggressive strategies — but the sector’s credibility should improve.
In the medium term, this may accelerate a hybrid model in which DeFi protocols integrate “compliance-ready” assets.
💡 Key insight
The Genius Act applies only to payment stablecoins.
Algorithmic stablecoins like UST or USDe remain outside the federal framework.
This limits systemic risks but may also slow down certain forms of innovation within DeFi.
Genius Act, STABLE Act and MiCA: Diverging Regulatory Visions
Comparison of the different approaches
| Criterion | GENIUS Act (US) | STABLE Act (US) | MiCA (EU) |
| Supervision | Federal + state-level | Strictly federal | Supranational (ESMA + national authorities) |
| Authorized issuers | Banks + licensed non-banks | Banks only | Licensed PSCA entities |
| Reserve requirements | 100% cash / Treasuries | 100% cash / Treasuries | 100% liquid assets |
| Interest allowed | No | No | No |
| Political objective | Support USD dominance | Protect the banking system | Harmonize the European market |
💡 Key takeaway
MiCA aims to create a stable and harmonized European digital-asset market.
The Genius Act is primarily designed to reinforce U.S. monetary dominance.
Global Regulatory Landscape for Stablecoins
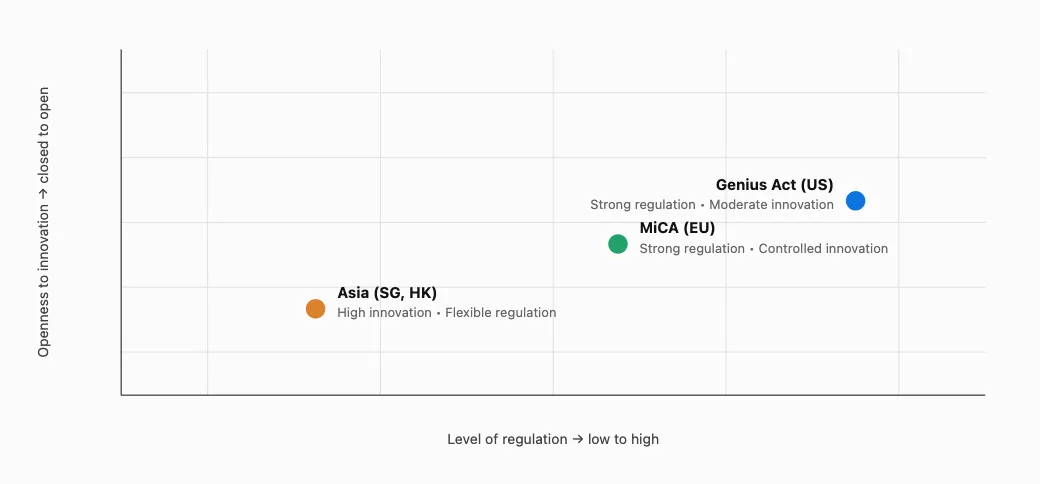
💡 Interpretation
The Genius Act fits within a U.S. model of controlled innovation.
Europe prioritizes legal harmonization and risk mitigation before broad adoption.
Asia remains the most experimental and open laboratory for digital-finance innovation.
Critiques and Controversies
Market Concentration
The Genius Act, by imposing high requirements in terms of reserves, audits, and compliance, could strengthen the position of already established players such as Circle or Tether, as well as that of financial institutions with robust regulatory infrastructures.
While this approach promotes stability, it nonetheless raises the question of market access for emerging players, whose ability to comply with these standards remains limited.
In the long term, some observers fear a risk of concentration in the issuance of regulated stablecoins, reducing diversity and competition within the ecosystem.
Macroeconomic Risks
The requirement to hold short-term U.S. Treasury securities as reserve backing provides a robust safety mechanism but is not free from systemic effects.
A sudden increase in demand for government securities could intensify pressures in the bond market, while an opposite movement—during massive redemptions—could amplify volatility.
These risks remain theoretical at this stage, and U.S. regulators have already indicated that they are closely monitoring the potential effects of this new dynamic on financial stability.
Let us also recall that the total amount of U.S. Treasury securities outstanding is around USD 30 trillion as of September 2025, compared to USD 300 billion for stablecoins. If the latter reach USD 1.6 trillion in circulation by 2030 (Citi’s median projection scenario), their issuers could then hold around 5% of U.S. Treasuries.
Conflicts of Interest and Governance
President Donald Trump’s involvement in promoting the Genius Act, while simultaneously supporting a stablecoin project through his structure World Liberty Financial, has raised questions about the neutrality of the legislative process.
Political leaders, including Senator Elizabeth Warren, are calling for a clearer separation between public action and private interests in the regulation of digital assets.
These debates reflect a broader issue: how to ensure impartial governance while supporting large-scale financial innovation?
💬 Key Takeaway
The Genius Act represents a major regulatory milestone, but its rollout will need to be monitored closely.
The success of this framework will depend on its ability to reconcile stability, fair access, and institutional trust—without hindering the innovative momentum that has shaped the stablecoin ecosystem.
What’s next?
Next steps
The Genius Act is only the first step toward the full structuring of the U.S. stablecoin market.
The coming months will be decisive:
- Legislative harmonization with the STABLE Act, still under discussion in the House of Representatives.
- First licenses issued by the Federal Reserve (Fed) and the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC), expected sometime in 2026.
- Progressive integration of these new standards into banking, fintech and treasury-management strategies.
These developments should define a new balance between innovation and oversight, where stablecoins become a recognized, integrated and supervised financial instrument.
Medium-term outlook
By 2026–2028, several trends are emerging:
- Regulated stablecoins establish themselves as genuine digital monetary instruments, supported by institutions.
- Decentralized finance continues its shift toward an institutional model, where protocols and regulated actors coexist.
- A lasting regulatory competition takes shape between the United States and Europe, each seeking to establish the global standard.
💡 In summary
The Genius Act marks a historic shift: stablecoins are moving out of the experimental domain and into the regulated financial sphere.
But this turning point raises a fundamental question:
Can decentralization be regulated without being distorted?
This will be the core challenge of the coming years — finding the right balance between control, trust and innovation.